Solar Energy
Solar energy is the hottest renewable energy source around the globe. Solar panel installations of all sizes are being rapidly deployed in many countries, such as China and Pakistan. But what is solar energy, and how does it work? Keep reading to find out!
What is solar energy?
Solar energy is energy harnessed from the sun’s light and transformed into electricity by solar panels. Solar is one of the fastest-growing renewable energy sources. More energy from the sun reaches the Earth’s surface in just a few hours than is used by everyone on the planet in a single year. New technologies and systems are continually being developed to capture all of this energy.
Solar energy is and will continue to be a key strategy to lower fossil fuel emissions and fight climate change. The key benefits of solar energy are that it (1) uses freely available energy from the sun, (2) produces zero emissions, and (3) can reduce energy bills.
Solar panels cover the slanted roof of St. Bartholomew’s Episcopal Church in Cambridge, MA. Photo: Climable, 2024
Solar panels cover the slanted roof of St. Bartholomew’s Episcopal Church in Cambridge, MA. Photo: Climable, 2024.
How do solar panels work?
Solar panels are made up of photovoltaic (PV) cells. PV cells are made of specific materials that can conduct electricity (known as semiconductor materials), like silicon. When the sun’s light hits the cells, electrons within the semiconductor materials are released and eventually converted into electricity.
PV cells are the building blocks of a solar panel. Alone, they can only produce a small amount of electricity. To provide more substantial power, multiple PV cells are connected to create modules. Multiple modules are then connected, forming panels. When multiple panels are connected, they’re called a solar array.
Solar panels and arrays can be sized to fit an installation area, like a roof or parking lot canopy, and the desired amount of electricity production. Solar panel production can be maximized by installing them in spots that receive as much sun as possible throughout the day and are not shaded by trees or other objects.
Some other factors that can impact how much energy solar panels produce and the benefits they generate are:
Weather: Clouds, rain, and snow can reduce the amount of sunlight reaching the panels, lowering their efficiency.
Efficiency: How much sunlight solar panels convert to electricity depends on the quality of the materials and technology used. More efficient panels can produce higher amounts of energy.
Ownership: Whether you own, lease, or participate in a community solar program can influence the financial benefits and responsibilities associated with solar energy.
How is solar energy used?
The energy generated from a solar array can be used to power a building, home, or industrial facilities, or even large geographical areas. On sunny days, a solar array may generate more electricity than can be used at the time. This extra energy can be stored in battery storage systems or sold to the local utility and distributed on the grid through programs generally called net metering.
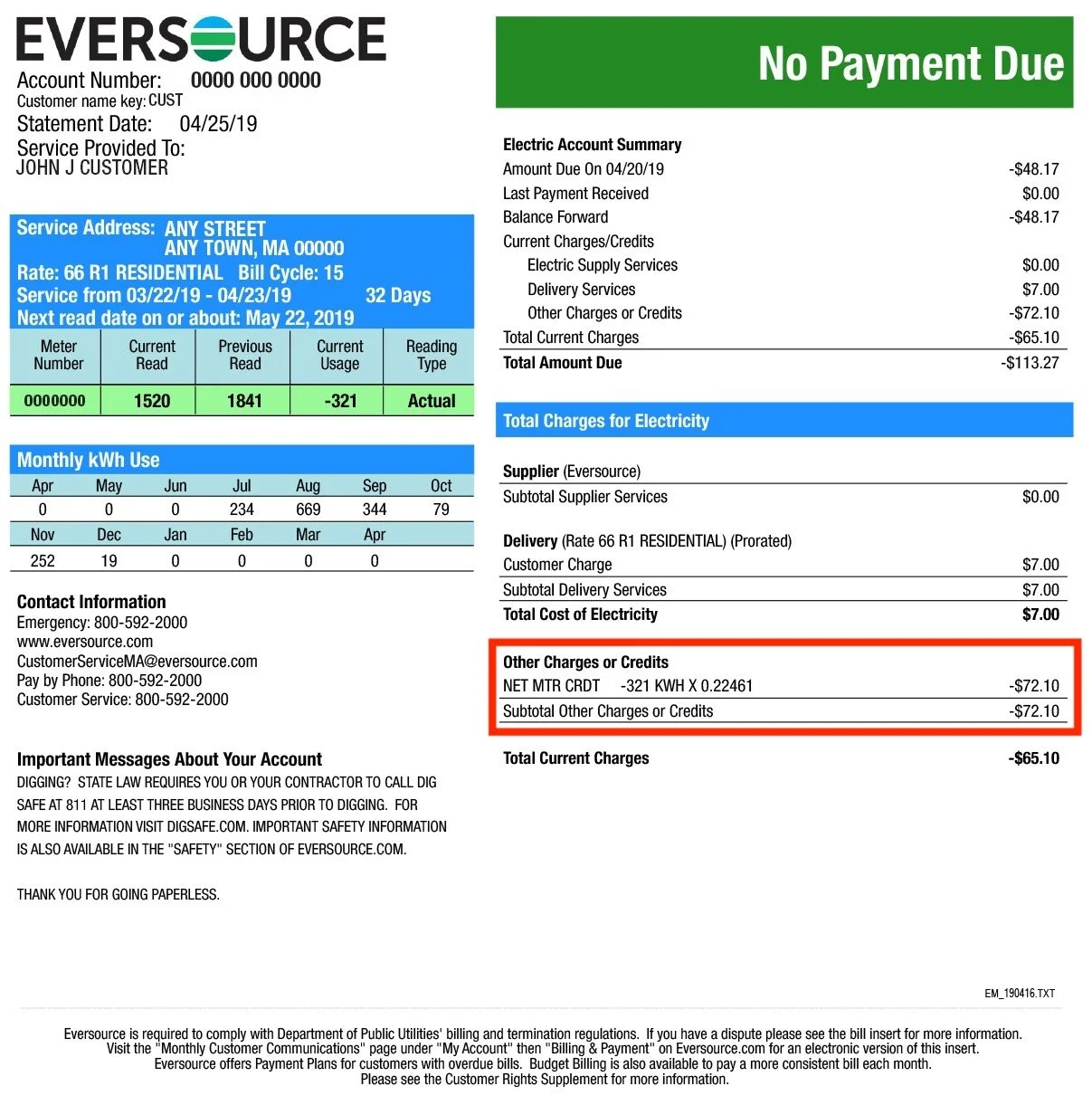
Net metering can save solar panel owners money on their electricity bills. Utilities subtract the amount of solar energy a customer sends to the grid within a billing period from the amount of energy they consumed, or used, over the same period. They provide on-bill credits for the solar energy generated, reducing the bills. The customer is then charged for the remaining amount of electricity used. However, if the customer generated more solar energy throughout the billing period than they used overall, they will not owe any money to the company. Check out this example below:
This is a mock Eversource electricity bill. The red box, located towards the bottom right, highlights the amount of money saved through net metering during the billing period. In this example, the household produced more electricity with their solar panels than they used in their house, resulting in a net credit of $65.10 after the $7.00 delivery charge is applied. This household, therefore, does not owe the utility Eversource any money for this billing period.
Image: Eversource, 2019
Battery storage can be added to enhance the benefits of solar panels. Sometimes, solar panels produce the most amount of electricity when we don’t need it. Batteries can help store excess energy until it’s needed, such as in the late afternoon or evening.
At Climable, solar panels and batteries are key components to our community microgrid model (read more here) to provide a local electricity source. We work with community-based organizations and municipal governments to add solar panels and batteries to facilities that provide necessary services for the community during an emergency. We connect these buildings into a virtual network, coordinating their usage of the energy in the solar panels and batteries. Our use of solar panels and battery storage in our community energy projects ensures a stable, cheaper, and cleaner energy source for urban communities.
Current landscape of solar energy
The US has established the ambitious goal of achieving carbon-free electricity generation by 2035. Individual states have also set emission reduction, clean energy, and renewable energy targets. For example, Massachusetts implemented the Solar Massachusetts Renewable Target (SMART) program and achieved its goal of installing 1600 MW of solar energy by 2020. Currently, almost 25% of the state’s electricity is generated by solar power.
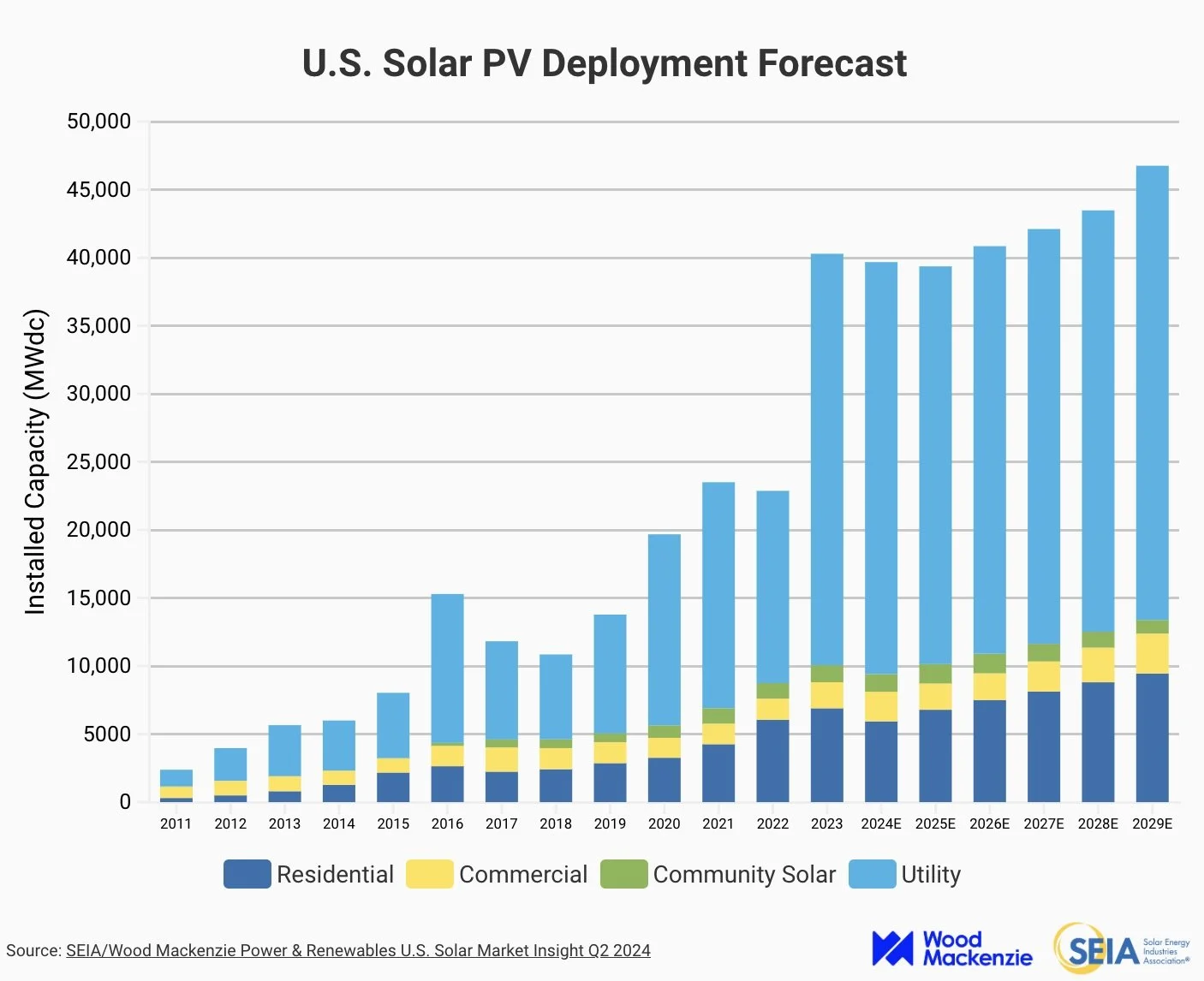
This graph shows the actual and predicted future amount of solar power in the US each year by sector, starting in 2011 and going through 2029. The general trend is an increase in solar in the US, with major gains having been made between 2011 and 2023, and steady gains predicted for the following 6 years.
Graph: Solar Industry Research Association (2024)
However, at a nationwide scale, the percentage of solar energy is much lower, making up only 4% of total electricity generated in the US. Solar energy is projected to increase, and is doing so around the globe at an exponential rate. In the US, political pressures are reshaping what the future might look like. Increasing solar energy is key to meeting the nation’s carbon-free electricity generation goals.
While Climable’s work focuses on community-owned solar solutions, privately-owned residential solar is also a key part of the energy transition. To learn more about adding solar to your home, check out this resource.